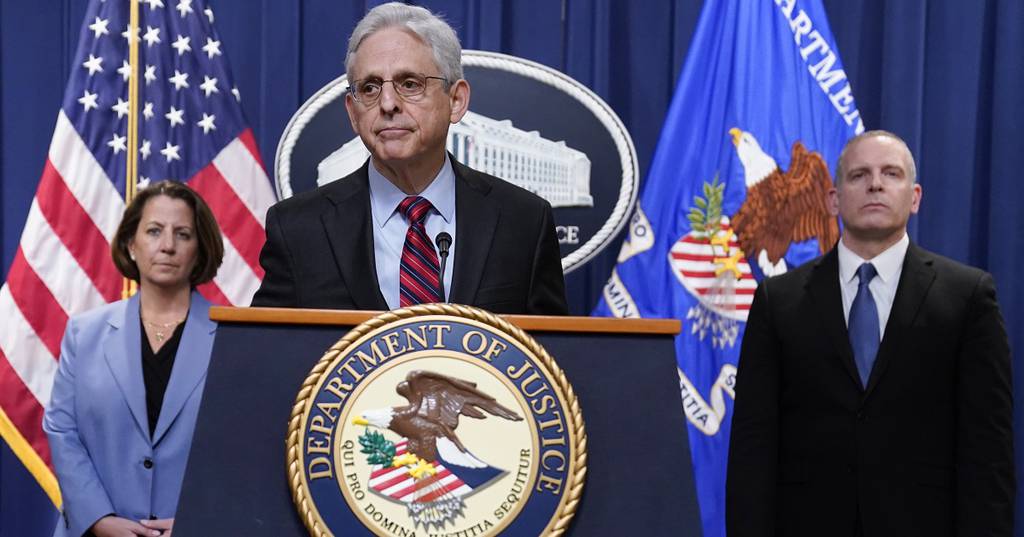
House Republicans grilled Attorney General Merrick Garland on Wednesday about the Justice Department investigation of Hunter Biden in a contentious hearing that delved into aspects of the criminal justice system that typically play out long before the case enters a public courtroom.
Many questions from members of Congress centered on the yearslong investigation of the president’s son, who has been under scrutiny for his business dealings and has now been indicted on a federal firearms charge alleging he lied about his drug use as he bought a gun in 2018.
Internal Revenue Service agents have claimed in whistleblower testimony the investigation was “slow walked” and the authority of the prosecutor in charge was curtailed by the Justice Department. Garland has strongly denied the allegations, but they could become a main line of attack as an impeachment inquiry into President Joe Biden unfolds.
While the Hunter Biden case is far from typical, it touches on some of the more mundane but less-well-understood aspects of the criminal justice system.
Here are some common questions and answers about the workings of criminal prosecutions:
How do cases get filed?
In the federal court system, cases typically start with investigators at agencies like the FBI, Drug Enforcement Administration or Homeland Security. There are 94 U.S. Attorney’s Offices where prosecutors look at evidence and decide whether to file charges. Some cases turn into criminal charges, while in others prosecutors decline to proceed. Prosecutors typically have wide discretion about who to charge, how many charges to file, and how serious those charges should be — and they may differ from counts investigators cited in an arrest or investigation.
What is an investigation crosses jurisdictions?
If authorities following leads in one case find allegations that cross into another state or jurisdiction and prosecutors want to file charges, there are at least two paths they can follow.
A U.S. attorney’s office can partner with counterparts in the other state and file the case together. If prosecutors in the other state decline to work together, a U.S. attorney can request permission to bring a case outside of his jurisdiction under what’s known at the Justice Department as a “515 order.”
The order – its name references a section of federal law – says the prosecutor has been directed to work in the other jurisdiction by the attorney general. Such an order, requiring approval in this case by Garland or another senior Justice Department official, gives the prosecutor what’s typically known as “special attorney” status.
In his testimony on Wednesday, Garland referred to that process as “very common” and “nothing cumbersome.”
In the Hunter Biden case, IRS agents have alleged that Delaware U.S. Attorney David Weiss, the prosecutor overseeing the case, was turned down by his counterparts in Washington and California when he wanted to file tax charges there. Republicans cite that as evidence that Weiss never had “full authority” to pursue the case. Garland acknowledged that U.S. attorneys can refuse to cooperate for reasons ranging from workload to their view of the strength of the case, but said that he quickly gave Weiss special status.
What is a special counsel?
A special counsel is an attorney who is appointed to investigate a case in which the Justice Department perceives itself as having a conflict or where it’s considered to be in the public interest to have someone outside the government come in and take responsibility.
This person is not subject to day-to-day supervision of the Justice Department, but must still comply with department regulations, policies and procedures. The attorney general is expected to give great weight to special counsels’ views, but can also seek explanations about any investigative or prosecutorial step they want to take. The attorney general retains final say and is the one government official who can fire them, but must notify Congress if a move the special counsel wants to make is rejected.
Republicans raised questions Wednesday about Weiss’s status as a special counsel appointed in August, saying a plea deal his office was ready to strike with Biden was a “sweetheart deal” and showed he wasn’t the best choice for the role. Garland, for his part, said he made the appointment because Weiss requested it and was leery of “changing horses midstream.”
He demurred on other questions about the timing of the decision, saying he didn’t want to share details of an ongoing investigation and had been purposely hands-off on the Hunter Biden probe in particular to avoid any perception of political interference.
What about the Hunter Biden case?
Congressional Republicans have been investigating nearly every aspect of Hunter Biden’s business dealings, as well as the Justice Department’s handling of his case. Several federal investigators have testified to having differing views of Weiss’ authority in the waning months of the investigations late last year.
Gary Shapley, a veteran IRS agent who had been assigned to the case, testified to Congress in May that he heard Weiss say in a October 2022 meeting that he was not the “deciding person whether charges are filed” against Hunter Biden.
But in the past two weeks, senior FBI agents Thomas Sobocinski and his deputy — two of seven people in attendance — told lawmakers that they have no recollection of Weiss saying that.
“At no point did I think he did not have that authority to do all of those steps with all that we were looking at,” Sobocinski said. He added later in the interview, “I never thought that anybody was there above David Weiss to say no.”
This post was originally published on this site be sure to check out more of their content.