InstaLinks : help you think beyond the issue but relevant to the issue from UPSC prelims and Mains exam point of view. These linkages provided in this ‘hint’ format help you frame possible questions ina your mind that might arise(or an examiner might imagine) from each current event. InstaLinks also connect every issue to their static or theoretical background. This helps you study a topic holistically and add new dimensions to every current event to help you think analytically
Table of Contents:
GS Paper 1:
- Impact of violence on a child’s Rights
GS Paper 4:
- Indian Theory of Materialism
Content for Mains Enrichment
- Mitti Café
Facts for Prelims (FFP)
- WHO’s Commission on Social Connection (2024–2026)
- Karmayogi Prarambh
- AGNI – ‘Ayurveda Gyan Naipunya Initiative’
- Amyloidosis
- Music frog
Mapping
- Nordic-Baltic (NB8) countries
AGNI – ‘Ayurveda Gyan Naipunya Initiative’
Facts for Prelims (FFP)
Source: PIB
Context: The Central Council for Research in Ayurveda Sciences (CCRAS), under the Ministry of Ayush, has launched the “Ayurveda Gyan Naipunya Initiative” (AGNI) to promote research and mainstream pragmatic practices in Ayurveda.
- AGNI aims to provide a platform for Ayurveda practitioners to report innovative practices and experiences in various disease conditions, fostering a culture of evidence-based practice.
- The initiative also seeks to identify interested practitioners for collaboration in creating a database and offers training in research methods.
The initiative aligns with CCRAS’s commitment to research on scientific lines in Ayurveda, and it complements other programs initiated by the organization, such as SPARK, PG-STAR, and SMART, aimed at promoting scientific research in Ayurveda.
Amyloidosis
Facts for Prelims (FFP)
Source: PIB
Context: Scientists from the Institute of Advanced Studies in Science and Technology have successfully fabricated a 2D protein monolayer using lysozyme molecules, a model protein for studying diseases like Amyloidosis.
- Amyloidosis is a rare condition where the accumulation of amyloid protein in organs leads to dysfunction in vital organs such as the heart, kidneys, liver, spleen, nervous system, and digestive tract.
- The study investigated the physical properties of lysozyme molecules at the air-water interface under varying surface pressure and subphase pH conditions.
- The compressible behaviour of lysozyme monolayers was correlated with the formation of stripe-like domains with increasing surface pressure.
Lysozyme is a naturally occurring enzyme that protects against bacteria, viruses, and fungi. It’s found in many bodily secretions, including:
Tears, Saliva, Milk, Sweat, Mucus, Egg white, Nasal mucus, Gastric secretions
Impact of violence on a child’s Rights
GS Paper 1
Syllabus: Indian Society
Source: TH
Context: The provided text discusses the impact of violence on a child’s mind, particularly in the context of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Recent examples of conflict affecting children:
- Current Gazan Crisis: Children form the majority of people killed during the conflict
- Syrian Civil War: The conflict in Syria has resulted in a humanitarian crisis, with millions of children affected by displacement, violence, and a lack of access to education and healthcare.
- Yemen Conflict: The conflict in Yemen has impacted children through malnutrition, lack of medical care, and exposure to violence.
- Rohingya Crisis: The persecution and displacement of the Rohingya population from Myanmar to Bangladesh have left many children in overcrowded refugee camps, facing inadequate living conditions and limited access to education.
- COVID-19 Pandemic: Lockdowns, school closures, and economic challenges have disproportionately impacted vulnerable children.
- Natural Disasters (e.g., Hurricanes, Earthquakes, Tsunamis): Events like hurricanes in the Caribbean, earthquakes in Nepal, and tsunamis in Southeast Asia have resulted in displacement, trauma, and disrupted access to basic necessities for children.
- Armed Conflict in Afghanistan: Decades of conflict in Afghanistan have led to the displacement of families, disrupted education, and exposure of children to violence.
- Various Civil Wars in Africa:g., The civil war in South Sudan has led to displacement, food insecurity, and disrupted access to education and healthcare for children.
Impact of conflict on children:
| Aspect | Description |
| Cycle of Revenge | Children experiencing conflict may harbour resentments and seek retribution. |
| Resistance to Social Norms | Adolescents exposed to violence may exhibit rebellious behaviour against societal expectations. |
| Psychological Trauma | Survivors of conflict zones may develop anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). |
| Impact on Education | Children in war zones may face disruptions in schooling, impacting academic performance and future prospects. |
| Long-term Consequences | Adults who experience violence in childhood may perpetuate violence or struggle with mental health challenges. |
| Recruitment and Use | Armed groups exploit children by coercing them into combat or support roles, compromising their well-being. |
| Sexual Violence and Exploitation | Conflict increases the risk of sexual violence, subjecting children to rape, trafficking, and other forms of exploitation. |
| Boys continued to be more affected by recruitment and use, killing and maiming, and abduction, while girls were disproportionately affected by conflict-related sexual violence. |
India’s Success in Protecting Children’s Rights:
For the first time since 2010, India has been removed from the 2023 United Nations Report on Children and Armed Conflict. This decision reflects the measures taken by the Indian government to safeguard children, particularly addressing previous accusations of recruiting and using boys in armed groups in Jammu and Kashmir (J&K).
Initiatives to Protect Children’s Rights
| Initiatives | Details |
| Infrastructure Establishment | Establishment of Child Welfare Committees, Juvenile Justice Boards, and Child Care Homes under the Juvenile Justice Act, 2015 in J&K. |
| UN-Recommended Measures | Implementation of UN-recommended measures, including training programs for security forces on protecting children. Suspension of pellet guns use in J&K |
| Enforcement of Acts | Active enforcement of the Juvenile Justice Act, 2015, and the Protection of Children from Sexual Offenses (POCSO) Act, 2012. |
| Global Conventions Compliance | Compliance with global conventions such as the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child (CRC), additional protocols to the Geneva Conventions, and the Optional Protocol on the involvement of children in armed conflict. |
| Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (ICC) | Recognition of recruiting child soldiers as a war crime under the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (ICC). |
| Recognition of the recruitment and use of child soldiers as one of six “grave violations” by the United Nations. | |
| Indian Legal Framework | India’s status as a party to the CRC and accession to the Optional Protocol. Inclusion of most CRC rights in the Indian Constitution. IPC criminalizes the recruitment or use of persons under 18 in hostilities. |
About UNCRC:
The United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child (UNCRC) is a globally recognized international agreement adopted in 1989 and enforced in 1990, with 54 articles outlining children’s rights and governmental responsibilities. Ratified by all UN members except the United States, it ensures children’s fundamental rights, including the Right to life, education, protection from abuse, the right to be heard, and a relationship with parents.
The core principles include non-discrimination, the right to life, survival, and development, the best interests of the child, and respect for the child’s views
Way Forward:
Trauma-Informed Responses: Countries should emphasize understanding the impact of past experiences on children in justice and protection systems. They should also encourage a comprehensive approach to address trauma in children in conflict with the law, using civil society organizations and Child groups.
Kailash Satyarthi, a Nobel Peace Prize winner known for his work in safeguarding children’s rights, condemns the harm inflicted on children in the conflict (the present Israel-Palestine conflict has profoundly affected both Israeli and Palestinian children)
WHO’s INSPIRE strategy against violence on children involves seven key strategies:
| Strategy | Description |
| Implementation and enforcement of laws | Involves enacting and enforcing laws, such as banning violent discipline and restricting access to alcohol and firearms. |
| Norms and values change | Aims to change societal norms and values, particularly those that condone behaviours like the sexual abuse of girls or aggressive behaviour among boys. |
| Safe environments | Identifies and addresses specific local causes of violence, often employing strategies like problem-oriented policing. |
| Parental and caregiver support | Provides training to young, first-time parents to enhance their ability to care for and nurture children effectively. |
| Income and economic strengthening | Includes initiatives like microfinance and gender equity training to improve economic stability, addressing underlying factors contributing to violence. |
| Response services provision | Ensures that children exposed to violence have access to effective emergency care and receive appropriate psychosocial support. |
| Education and life skills | Focuses on promoting school attendance and providing life and social skills training for children, contributing to their overall well-being and resilience. |
Conclusion:
Montessori, in “The Secret of Childhood” (1936), emphasized the importance of peaceful childhood circumstances, asserting that major individual and social issues originate from early years and therefore need concerted efforts to shield children from the effects of conflicts.
Insta Links:
Indian Theory of Materialism
GS Paper 4
Syllabus: Ethical Philosophy
Source: TH
Context: The article explores Indian Materialism, highlighting its historical roots and key philosophical tenets.
What is Philosophy (‘Darshan’ in Sanskrit)?
Philosophy seeks to explain the universe and guide human actions with a comprehensive worldview
What is Materialism (Bhautikvad)?
Materialism is a philosophical concept asserting that the fundamental substance of reality is “matter.” It posits that everything that exists, including thoughts and consciousness, can be explained in terms of physical entities. In essence, it contends that the origin of all that exists is rooted in tangible, physical substances rather than abstract or spiritual elements.
Origin of Materialism?
- In ancient India, the Lokāyata school, also known as Carvaka, was one of the earliest materialist traditions, asserting that reality is composed solely of physical elements and rejecting metaphysical or supernatural entities.
- In ancient Greece, philosophers like Democritus and Epicurus embraced materialistic ideas, proposing that the basic constituents of the universe are material particles.
Various Schools of Indian Materialism:
| Schools | Key Tenets | Figures |
| Lokāyata | Rejects the existence of a soul or afterlife. – Emphasizes perception as the only valid source of knowledge. Advocates hedonism and the pursuit of pleasure. | Brhaspati, Ajita Kesakambali, Jābāli |
| Charvaka | Asserts that only the perceptible world is real. – Denies the validity of inference and metaphysical concepts. – Advocates a naturalistic and pleasure-oriented life philosophy. | Brihaspati (attributed to the founder of Charvaka philosophy) |
| Bhautikavad | Stresses the material nature of reality (Bhautika). Considers physical elements as the fundamental constituents of the world. | |
| Jadavada | Focuses on investigating the material or inert (jada) aspect of existence. Emphasizes understanding the root or origin of things. | |
| Dehatmavada | Identifies the self (atman) with the body (deha). Rejects the duality of self and body, considering them as one entity. | |
Various applications of Materialism:
| Materialist Views | Key Points |
| Perception as Knowledge Basis | Materialists consider perception as the foundational source of knowledge. Direct sensory experiences form the basis for understanding the world. |
| Use of Inference | Contrary to some misconceptions, materialists employed logical inference based on perceptual evidence. |
| Disregarding Divine Agency | Materialists rejected the notion of divine providence and supernatural realms. |
| Emphasis on Pleasure | The pursuit of happiness and pleasurable experiences is considered a valid and important aspect of human existence. |
| Living in the Present | The principle “yāvat jīvēt sukham jīvēt” advocates for living a fulfilling present life. Materialists valued the importance of enjoying life in the here and now without being overly concerned about an afterlife. |
| Human-Created Values | Materialists view values as human constructs, independent of divine morality. Ethics and values are seen as products of human experience and societal development, rather than imposed by a divine authority. |
| Action and Responsibility | Materialists stress the impact of one’s actions on themselves and the world. Ethical conduct and responsibility for one’s actions are emphasized as essential aspects of a meaningful and fulfilling life. |
| Earthly Heaven and Hell | Materialists redefined heaven and hell in earthly terms. Heaven is perceived as enjoying life’s luxuries, akin to the gods’ enjoyment in mythological heavens. Hell is seen as earthly suffering, such as diseases and hunger. |
Critics of Materialist theory
It oversimplifies the complexity of human experience by reducing everything to material phenomena. They contend that it neglects the spiritual or transcendent aspects of life, undermines moral and ethical considerations, and may lead to a hedonistic worldview. Additionally, opponents argue that materialism struggles to account for consciousness, subjective experiences, and aspects of reality beyond the physical realm.
Despite criticism, Materialism is important in present times:
The materialist theory remains relevant in present times for its emphasis on empirical evidence, rationality, and a focus on improving the human condition without reliance on supernatural explanations. It provides a framework for understanding the world, promoting ethical conduct, and valuing the present life, aligning with modern principles of science, secularism, and humanism.
Insta Links:
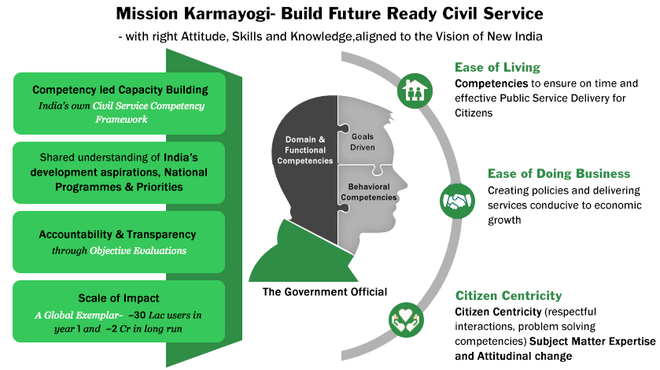
Karmayogi Prarambh
Facts for Prelims (FFP)
Source: PIB
Context: Karmayogi Bharat, launched last year, celebrated the first anniversary of Karmayogi Prarambh, an online orientation program on the iGOT Karmayogi Platform for government appointees recruited through Rozgar Melas.
- The program, consisting of eight curated courses, aims to help new government employees acclimatize to policies and transition smoothly into their roles.
- The iGOT Karmayogi platform is a comprehensive online learning portal for capacity-building among government officials, with over 26 lakh learners currently registered and access to 815+ courses.
- The Karmayogi Prarambh courses cover topics such as Code of Conduct for Government Employees, Prevention of Sexual Harassment of Women in the Workplace, Understanding Motivation, Self-Leadership, Stress Management, Effective Communication, MS Word for Beginners, and MS Excel for Beginners.
Mitti Café
Content for Mains Enrichment
Source: TH
Context: Mitti Cafe, a social initiative by the Mitti Social Initiative Foundation, has opened a 750-square-foot cafe within the premises of the Supreme Court of India. Inaugurated by Chief Justice DY Chandrachud, the cafe features decor and furniture made by persons with disabilities and their caregivers.
Mitti Cafe, dedicated to providing employment to persons with disabilities, operates 41 cafes across India and has sold over 11 million meals, employing 4,000 individuals with disabilities. The collaboration with the Supreme Court aims to break stigmas around disability and promote diversity and inclusion. The cafe’s menu is also available in Braille.
Usage: The example of Mitti Cafe reflects ethical values such as inclusivity, diversity, and social responsibility.
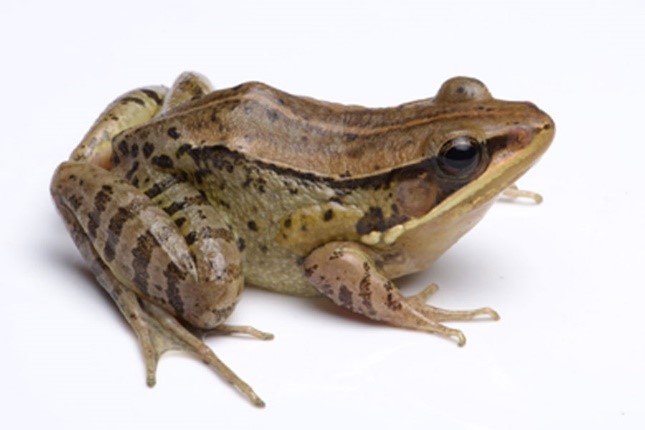
Music frog
Facts for Prelims (FFP)
Source: TH
Context: Scientists have identified a new species of ‘music frog,’ named Nidirana noadihing, in Arunachal Pradesh.
- This unique discovery is marked by the distinct feature that both male and female frogs are vocal.
- The frogs emit a distinctive call pattern consisting of two to three notes, resembling the sounds of wild duck species.
- The male frogs, characterized by their robust bodies, were observed calling loudly in various locations, including marshy areas, the edges of a newly constructed pond, and along a nearby road.
- The frog is named after the Noa-Dihing River where it was found.
The findings confirm the presence of the Nidirana genus in India for the first time, with previous known occurrences in Japan, Taiwan, China, Vietnam, Laos, and Thailand.


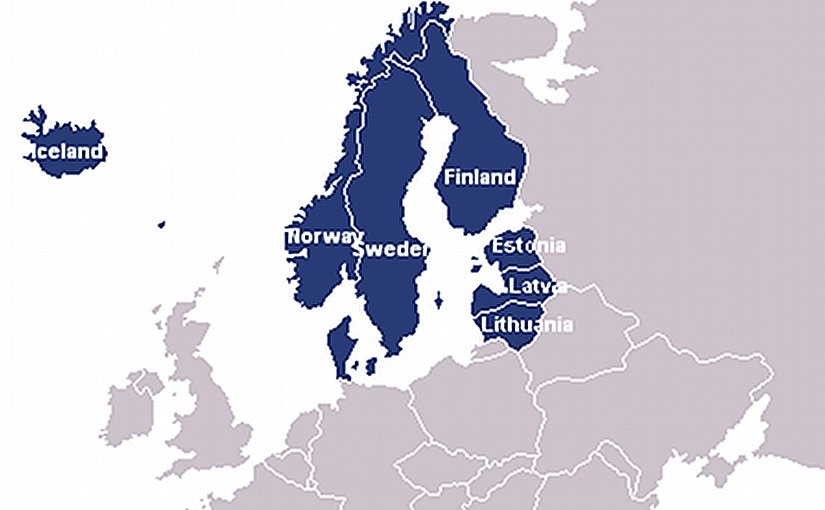
Nordic-Baltic (NB8) countries
Mapping
Source: MEA
Context: India’s External Affairs Minister commended the CII for hosting the 2nd India Nordic Baltic Business Conclave, highlighting the increasing collaboration between India and the Nordic-Baltic (NB8) countries.
What is NB8?
The Nordic-Baltic (NB8) countries refer to a group of eight nations in Northern Europe, comprising the Nordic countries (Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden) and the Baltic states (states along the Baltic Sea) (Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania). These countries collaborate on various economic, diplomatic, and strategic initiatives to promote regional cooperation and address shared challenges.
This region is characterized by close geographical proximity and shared historical, cultural, and economic ties. It serves as a platform for collaboration and partnership among the countries in areas such as trade, innovation, and diplomatic relations.

WHO’s Commission on Social Connection (2024–2026)
Facts for Prelims (FFP)
Source: WHO
Context: The World Health Organization (WHO) has launched a Commission on Social Connection, co-chaired by U.S. Surgeon General Dr. Vivek Murthy and African Union Youth Envoy Chido Mpemba.
What is the Commission on Social Connection (2024–2026)?
It is a 3-year initiative to address loneliness as a global health threat. The Commission consists of 11 policy-makers and advocates. It aims to analyse the role of social connection in health, well-being, economic progress, social development, and innovation.
The Commission seeks to define a global agenda on social connection, raise awareness, and collaborate on evidence-based solutions, with a focus on the impact of loneliness across various age groups and income levels.
The article is to be read in combination with the previous article: Loneliness a Significant Global Health Threat
Download the Daily Current Affairs in PDF Format here
Follow us on our Official TELEGRAM Channel HERE
Subscribe to Our Official YouTube Channel HERE
Please subscribe to Our podcast channel HERE
Official Facebook Page HERE
Follow our Twitter Account HERE
Follow our Instagram Account HERE
Follow us on LinkedIn: HERE
This post was originally published on this site be sure to check out more of their content.