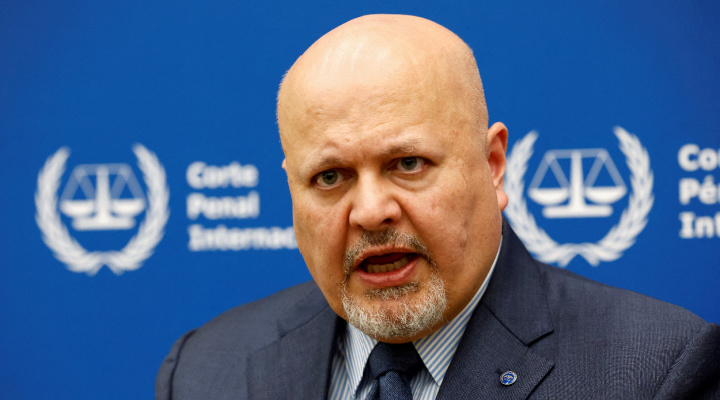
International Criminal Court Prosecutor Karim Khan speaks during an interview with Reuters in The Hague, Netherlands, Feb. 12, 2024. Photo: REUTERS/Piroschka van de Wouw
Due to the sheer volume of recent news stories concerning Israel, you may have missed two mostly unnoticed but important developments regarding Israel in the world of international law.
In the International Court of Justice (ICJ), South Africa has been suing Israel for genocide. I’ve been saying for months that South Africa does not have a case, but that the lawsuit is nonetheless dangerous because South Africa’s goal is not to win. Instead, its goal is to achieve an “emergency injunction” that would stop Israel’s campaign against Hamas, effectively handing the terror organization a victory.
Such an injunction would not require actually proving the claims against Israel, and so the emergency injunction has always been South Africa’s (and Hamas’) best chance of effectively defeating the IDF.
South Africa has made two unsuccessful attempts to obtain emergency orders, and is now coming up against an October 28 deadline to, at long last, submit their actual evidence of “genocide.”
Last week, South Africa petitioned the ICJ for an extension of several months, apparently because (unsurprisingly) they have not succeeded in finding such evidence.
While this is a small vindication, it is by no means the end of the story. The ICJ is only nominally a “court,” but in reality, functions as a political body. The ICJ’s current President is Nawaf Salam of Lebanon, which is effectively controlled by the Iranian backed Hezbollah terror organization and is actively at war with Israel. The ICJ judges include representatives from countries that have recently demonstrated strongly anti-Israel agendas, such as China and Brazil, as well as South Africa — the very country that’s suing Israel. Even the US delegate to the court has voted consistently against Israel in recent decisions.
In fact the only judge who has stood both firmly and eloquently in favor of Israel is the court’s Vice President, Julia Sebutinde of Uganda.
So while logic dictates that South Africa should not be able to win a lawsuit without evidence, politics has no such limitations. Israel has been petitioning the United States Congress for support in pressuring the ICJ to drop their case, and so has my organization.
An entirely separate international body is the International Criminal Court (ICC), in which prosecutor Karim Khan has petitioned the court to issue arrest warrants against Israeli Prime Minister Netanyahu, Defense Minister Yoav Gallant, as well as several Hamas leaders (two of whom are now dead).
The court has been deliberating the request since May, and last week, Khan issued a new request that the court issue the arrest warrants “urgently.”
It is not clear why such arrest warrants are now more urgent than before, yet some Israeli sources are concerned that the ICC may be sympathetic to the prosecutor’s request anyway. There is some speculation that this “urgency” may be designed to preempt Benjamin Netanyahu’s speech to the UN General Assembly later this month.
Much like the emergency orders in the ICJ, these ICC arrest warrants do not actually require proof. Instead, the prosecutor needs to provide only minimal evidence that his claims are reasonably possible, and he gets to do so “ex parte” — which means alone and without Israel having the opportunity to respond.
Like the ICJ, the ICC is also primarily a political body in the guise of a “court,” and therefore, sufficiently dramatic claims against Israel, especially when presented “ex parte” and with the right political pressure, may be adequate to persuade the judges.
Why does all of this matter? Here’s just one example: since the election of the Labor government, the UK has removed its objection to the ICC proceedings, and this month suspended the shipment of certain military items to Israel, in what amounts to essentially a “soft embargo.” The items in question include important parts for military equipment, such as the F-35 fighter jet, which wears out quickly and need constant replacement. Such parts are manufactured in only a few factories in the entire world and cannot be easily replaced.
Why doesn’t Israel make the parts itself? The factories are so specialized that even if Israel started building one today, it would take years and billions of dollars before production could even begin. Even “Israeli” inventions, such as the Merkava tank, make use of these specialized parts from foreign sources. In short, for the foreseeable future Israel depends on foreign resources to keep the IDF working.
If a relevant international body such as the ICJ were to make a ruling against Israel, instead of seeing a “soft embargo” of some military equipment by some countries, we might see official worldwide embargoes encompassing all equipment.
In as little as several months, as equipment begins to fail, the IDF could run out of working jets, helicopters, tanks, and all of the other tools necessary for the IDF to function as an actual army. Israel would become defenseless, not only against even a weakened Hamas, but also against Iran and all of its various proxies.
This reality relates to may other issues. For example, in the recent debate over whether Israel should abandon the Philadelphi corridor as part of a hostage deal, some IDF generals claim that Israel can simply retake it “at any time.” Yet when IDF generals speak about Israel’s capabilities, they usually refer only to military tactics and strategy, and often overlook the geopolitical forces that could strip the IDF of its capacity to function.
If Israel were to enter an internationally binding agreement (for example over Philadelphi) and then violate it, these kind of embargoes are just one possible consequence.
For this reason, we are keeping a close eye on activities at the ICC, the ICJ, the United Nations, the US Congress, and all the various bodies that have significant influence over Israel’s long term safety, and are actively involved in petitioning those bodies as well.
Daniel Pomerantz is the CEO of RealityCheck, an organization dedicated to deepening public conversation through robust research studies and public speaking.
This post was originally published on this site be sure to check out more of their content.